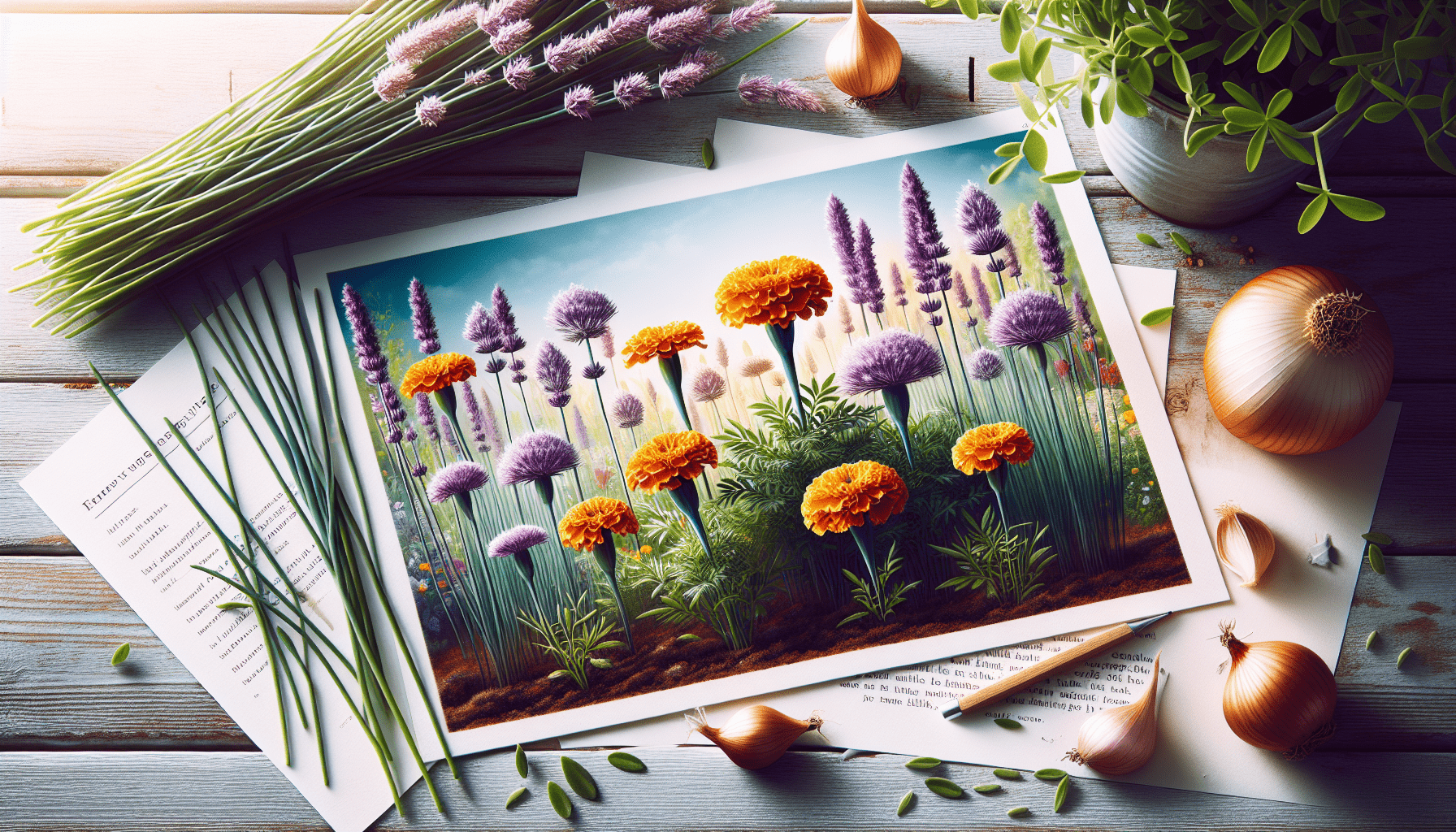
Companion Planting For Flowers: Maximizing Growth And Pest Control
If you’re a flower enthusiast looking to boost the growth and beauty of your garden, companion planting may just be the solution you’re seeking. Companion planting involves strategically placing certain plants together to maximize growth, deter pests, and promote overall garden health. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of companion planting specifically for flowers, sharing some key combinations that can make a remarkable difference in your garden. So, grab your gardening gloves and get ready to discover the secrets of companion planting for flowers. Let’s dive right in!

Companion Planting Basics
Definition of companion planting
Companion planting is a gardening technique that involves growing different plants in close proximity to one another for their mutual benefits. In this symbiotic relationship, each plant provides something that the other needs, such as pest control, improved growth, or enhanced pollination. By strategically selecting companion plants, gardeners can create a healthier and more productive garden ecosystem.
Benefits of companion planting
Companion planting offers a multitude of benefits for flower growth. One of the main advantages is pest control. By planting certain flowers alongside specific plants, you can deter common flower pests and minimize the need for chemical insecticides. Additionally, companion plants can enhance flower growth by attracting beneficial insects for pollination and providing natural shade or support for the flowers. Another benefit is soil improvement, as certain companion plants can help break up compacted soil or provide essential nutrients.
Factors to consider when selecting companion plants
When selecting companion plants for your flowers, it’s important to consider several factors. First, look at the specific needs of your flowers. some flowers prefer full sun, while others thrive in partial shade. Choose companion plants that have similar light and water requirements to ensure compatibility. Additionally, consider the maturity and growth habits of both plants. Make sure they won’t compete for space or resources as they grow. Finally, think about the pest and disease resistance of each plant. Select companion plants that have natural properties to repel common pests or suppress diseases that may affect your flowers.
Examples of successful companion plant combinations
There are numerous successful companion plant combinations that can boost flower growth. For example, marigolds and petunias make excellent companions for many flowers due to their ability to repel aphids and nematodes. Sunflowers and cosmos attract beneficial insects like bees and butterflies, promoting pollination and enhancing flower production. Pairing lavender with roses can help deter Japanese beetles, which are notorious for damaging rose plants. These are just a few examples of successful companion plant combinations, and the possibilities are virtually endless.
Companion Plants for Flower Growth
Plants that enhance flower growth
Several plants are well-known for their ability to enhance flower growth when planted nearby. Some popular options include borage, which attracts pollinators and improves overall plant health, and nasturtiums, which can repel aphids and other pests that may damage flowers. Sweet alyssum is another great choice, as it provides ground cover and attracts beneficial insects, increasing the chances of successful pollination.
Companion planting techniques for maximum flower production
To maximize flower production, certain companion planting techniques can be employed. One effective technique is interplanting, where flowers are mixed with herbs or other compatible plants in the same bed. This creates a diverse ecosystem that attracts a wide range of pollinators and beneficial insects. Another technique is creating mixed borders, where a variety of flowers and companion plants are arranged together to create a stunning display and increase pollination opportunities.
Implementation tips for successful flower growth
To ensure successful flower growth through companion planting, it’s essential to consider a few implementation tips. First, research the specific needs of your flowers and select companion plants accordingly. Make sure they have similar growth requirements in terms of sun exposure and water needs. Additionally, pay attention to spacing between plants. Proper spacing allows for good air circulation and prevents overcrowding, which can lead to disease and pest issues. Regularly monitor the garden for any signs of plant stress or pest infestation and take appropriate action promptly.
Companion Plants for Pest Control
Plants that repel common flower pests
One of the most significant benefits of companion planting for flowers is its ability to naturally repel common pests. Several plants are particularly effective in deterring pests and can be beneficial to have around flowers. For example, planting garlic or chives near roses can help repel aphids, while planting marigolds near tomatoes can deter nematodes. Nasturtiums are known to repel whiteflies and squash bugs, making them an excellent companion for a variety of flowers.
Companion planting strategies for pest prevention
To effectively prevent pests through companion planting, it’s important to strategize and plan your garden layout accordingly. Start by identifying the specific pests that commonly affect your flowers and research which companion plants are effective at repelling those pests. Implement companion planting by sowing the repellent plants in close proximity to the susceptible flowers. By strategically placing the companion plants, you can create a natural barrier or confuse the pests, reducing their impact on your flowers.
Natural pest control methods using companion plants
Companion planting for pest control goes beyond simply repelling insects. It also involves attracting beneficial insects that act as natural predators to the pests. For example, planting dill or fennel near flowering plants can attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on aphids and other harmful pests. Another useful technique is planting yarrow or daisies, which attract hoverflies and parasitic wasps that are known to prey on caterpillars and aphids.
Complementary Plant Associations
Combinations that promote pollination
To ensure successful pollination in your flower garden, consider companion plant combinations that attract pollinators. Bees, butterflies, and other insects play a crucial role in pollination. Certain plants, such as lavender, bee balm, and coneflowers, are particularly attractive to pollinators and can encourage them to frequent your garden. By planting these companions alongside your flowers, you increase the chances of successful pollination and subsequent fruit or seed development.
Attracting beneficial insects with companion plants
In addition to pollinators, it’s beneficial to attract other beneficial insects to your flower garden. These insects act as natural predators, feeding on pests that can harm your flowers. For example, planting dill or parsley near your flowers can attract predatory wasps and hoverflies, which help control aphid populations. Other plants like yarrow, tansy, and fennel can also attract beneficial insects that prey on various pests.
Companion planting for soil improvement
Companion planting can also contribute to soil improvement in your flower garden. Certain plants have deep taproots that help break up compacted soil, allowing better water penetration and root development for your flowers. For instance, planting daikon radishes near your flowers can help alleviate soil compaction. Additionally, leguminous plants like clover and beans can fix nitrogen in the soil, providing a nutrient boost to neighboring flowers.
Successful plant associations for color schemes and aesthetics
Companion planting is not solely about improving growth and pest control; it can also enhance the visual appeal of your flower garden. By selecting companion plants with complementary colors, textures, and heights, you can create stunning combinations that add interest and beauty to your garden. For instance, pairing purple salvia with yellow marigolds or orange cosmos can create an eye-catching display of contrasting colors. Consider the overall aesthetics when planning your companion planting scheme.

Companion Planting Techniques
Interplanting flowers with herbs
One effective companion planting technique is to interplant flowers with herbs. Herbs not only provide interesting foliage and aromatics, but they can also help repel pests and attract beneficial insects. For example, planting basil near roses can deter aphids, while rosemary can help repel snails and slugs. By interplanting herbs with flowering plants, you create a diverse garden ecosystem that supports various species and enhances overall garden health.
Creating mixed borders with compatible plants
Another technique for companion planting is creating mixed borders with compatible plants. This involves planting a mix of flowers and companion plants along the borders of your garden beds or pathways. By combining plants with similar growth habits, you can create a visually appealing border that attracts pollinators and other beneficial insects. For instance, planting tall sunflowers alongside shorter marigolds can create an attractive border that provides shade and support for the marigolds.
Succession planting for continuous flower blooms
To ensure continuous flower blooms throughout the growing season, consider using succession planting techniques. Succession planting involves planting different flower varieties at staggered intervals, so as one variety finishes blooming, another is ready to take its place. By including companion plants in your succession planting plan, you can maintain a consistent supply of flowers for your garden and prolong the blooming season.
Intercropping to maximize garden space
Intercropping is a technique that involves planting different crops or flowers in close proximity to maximize garden space. This can be particularly beneficial in small gardens or limited planting areas. By intercropping compatible flowers and companion plants, you can make the most of your available space. For example, interplanting lettuce with flowers like marigolds or bachelor’s buttons can help repel pests while maximizing garden productivity.
Companion Planting Planning and Layout
Designing a companion planting scheme
To successfully implement companion planting in your flower garden, it’s crucial to design a well-thought-out companion planting scheme. Start by considering the specific needs and growth habits of your flowers. Research companion plants that can benefit your particular flower varieties and make a list of potential combinations. Take into account factors such as light requirements, water needs, and compatibility in terms of pest control. Sketch out a garden plan that incorporates these companion plants and ensures optimal growing conditions for your flowers.
Arranging plants based on growth and height
When arranging companion plants, it’s important to consider their growth habits and height. Place taller plants in the back or center of the garden bed, ensuring they won’t shade or overcrowd shorter companion plants. This arrangement allows for better sunlight exposure and minimizes competition for resources. Additionally, consider the spreading habits of certain plants and leave enough space between them to avoid overcrowding and potential disease issues.
Mapping out a garden plot for companion planting
Mapping out your garden plot is an essential step in successful companion planting. Start by measuring the dimensions of your garden area and dividing it into sections or beds. Take into account any existing structures, such as fences or trellises, that can provide support for climbing or trailing companion plants. Consider the overall layout and flow of your garden, ensuring easy access for maintenance and harvesting. Use your companion planting scheme and knowledge of plant requirements to strategically place each plant in the designated areas.
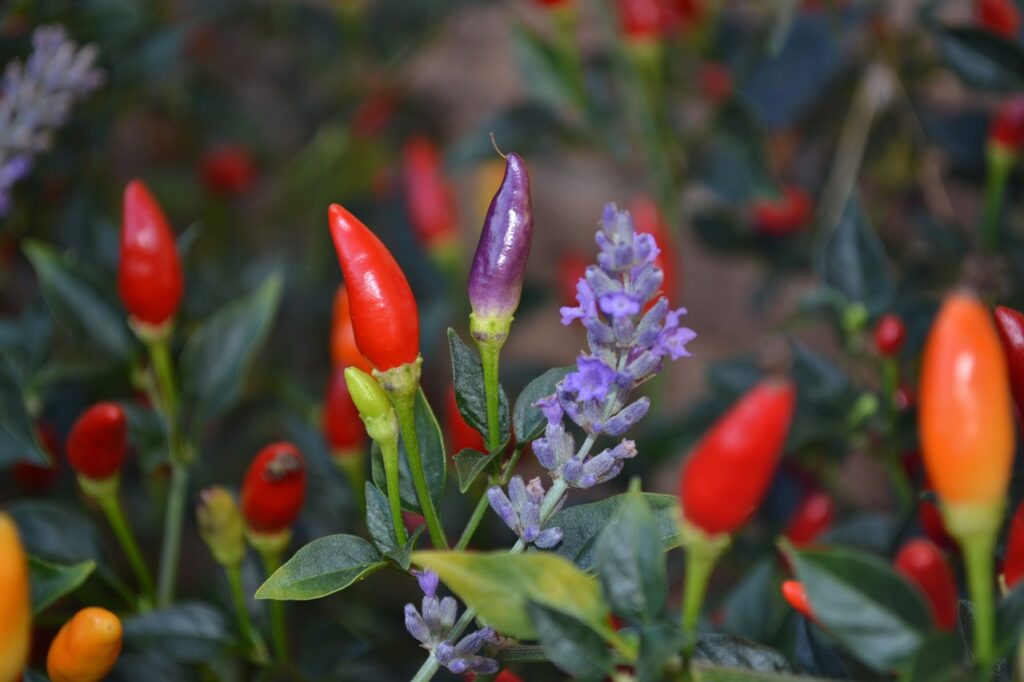

Companion Planting for Specific Flower Varieties
Companion plants for roses
Roses are a beloved flower, and pairing them with the right companion plants can enhance their growth and beauty. Some suitable companions for roses include lavender, which can repel pests like Japanese beetles, and geraniums, which help deter aphids. Additionally, planting chives near roses can help prevent blackspot, a common fungal disease that affects roses.
Best companions for daisies
Daisies are cheerful flowers that can benefit from companion planting. Planting yarrow or tansy near daisies can attract beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, that prey on aphids and other pests. Coreopsis and shasta daisies can also be great companions for other varieties of daisies, creating a stunning display of vibrant colors and attracting pollinators.
Enhancing the growth of sunflowers through companions
Sunflowers are known for their impressive height and vibrant blooms. To enhance the growth of sunflowers, consider planting companions that provide support or deter pests. Tall-growing plants such as corn or amaranth can provide natural support for sunflowers and create an eye-catching combination. Marigolds and borage are also excellent companions for sunflowers, as they attract pollinators and deter insects that may damage the sunflower plants.
Specific companion plants for various types of flowers
Different flowers have different companion plant preferences. For example, cosmos can benefit from the companionship of zinnias, marigolds, or alyssum, which attract a variety of beneficial insects. Peonies can thrive alongside lamb’s ear or catmint, which can provide shade and repel deer. When selecting companion plants for specific flower varieties, consider their individual needs and characteristics to create a harmonious and beneficial planting combination.
Common Challenges in Companion Planting for Flowers
Identifying potential issues
While companion planting for flowers offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential challenges. Identifying potential issues can help you address them promptly and effectively. Monitor your flower beds regularly for signs of nutrient deficiency, disease, or pest infestation. Observe any negative interactions between companion plants, such as overcrowding or shading issues. By being proactive and observant, you can prevent potential problems before they become more significant challenges.
Overcoming competition for resources
Competition for resources, such as water, sunlight, and nutrients, can be a common challenge in companion planting. Some companion plants may have more aggressive growth habits or higher nutrient requirements, potentially outcompeting your flowers. To overcome this challenge, provide adequate spacing between plants, ensuring each one has enough room to access the necessary resources. Regularly monitor and adjust the spacing as the plants grow to maintain a healthy balance.
Dealing with allelopathic effects
Allelopathy refers to the chemical interaction between plants, where certain plants release substances that can inhibit the growth of others. This can be a challenge in a companion planting scenario, as some plants may release chemicals that negatively affect neighboring flowers. To address allelopathic effects, research the specific plants you plan to include in your companion planting scheme. Choose companion plants that have compatible allelopathic tendencies or avoid planting incompatible combinations in close proximity.
Preventing cross-pollination between incompatible flowers
Cross-pollination between incompatible flower varieties can result in unwanted hybridization and impact the purity of specific flower types. To prevent cross-pollination, it’s important to consider the reproductive habits of your flowers and plan your companion planting scheme accordingly. Separate incompatible flowers either by distance or by timing their flowering periods to minimize the chances of cross-pollination. This will help preserve the true characteristics of each flower variety.

Experimental and Alternative Companion Planting Methods
Innovative techniques for companion planting
Gardening enthusiasts and experts are constantly exploring innovative techniques for companion planting. One such technique is the use of trap crops, which involves planting sacrificial companion plants that attract pests away from your desired flowers. These sacrificial plants can be removed or treated to control the pests without harming the main flower crop. Another innovative method is the use of living mulches, which involves planting low-growing companion plants between rows of flowers to suppress weeds and enhance soil health.
Unconventional plant combinations
In companion planting, the possibilities are not limited to traditional combinations. Some gardeners have experimented with unconventional plant combinations and reported success. For instance, pairing tomatoes with basil is a classic combination due to their compatibility and mutual beneficial properties. However, some gardeners have reported beneficial interactions between tomatoes and flowers like marigolds or petunias. While unconventional, these combinations can offer unique benefits and add diversity to your garden ecosystem.
Exploring novel research in companion planting for flowers
Researchers continuously explore the world of companion planting, providing gardeners with new insights and findings. Stay informed about the latest research in companion planting for flowers by reading gardening publications, attending workshops or webinars, and connecting with gardening communities. Novel research can shed light on new companion plant combinations, innovative techniques, and additional benefits that can further maximize growth and pest control in your flower garden.
Conclusion and Final Tips
Recap of the benefits of companion planting for flowers
Companion planting for flowers offers a wide range of benefits. It promotes natural pest control, enhances flower growth, improves pollination, attracts beneficial insects, enhances soil health, and adds aesthetic appeal to your garden. By strategically selecting and pairing companion plants, you can create a thriving and harmonious garden ecosystem that will benefit your flowers and the overall health of your garden.
Final advice for successful companion planting
To ensure successful companion planting for your flowers, consider the specific needs and characteristics of each plant. Research companion plants that are known to have beneficial properties and can support the growth of your flowers. Plan your garden layout and companion planting scheme carefully, taking into account factors such as light requirements, water needs, compatibility in terms of pest control, and height variations. Regularly monitor your garden, make adjustments as necessary, and maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Continuing exploration of companion planting for ongoing garden improvement
Companion planting is a dynamic and ever-evolving practice in gardening. As you gain experience and confidence, continue exploring and experimenting with different companion plant combinations. Keep yourself updated on new findings and techniques in companion planting through research and engagement with gardening communities. By embracing a spirit of curiosity and ongoing exploration, you can continuously improve your garden and enjoy the multitude of benefits that companion planting offers for your flowers.