Organic Pest Control For Flowers: Natural Ways To Protect Your Garden
If you’re a proud gardener, you know how frustrating it can be to see your beautiful flowers fall victim to pests and insects. But before you reach for harsh chemical pesticides, consider the benefits of organic pest control. In this article, we will explore some natural ways to protect your garden and keep your flowers thriving. From using beneficial insects to implementing companion planting techniques, we will cover all the tools you need to keep those pesky pests at bay without harming the environment. So, if you’re ready to embrace eco-friendly solutions for your garden, read on to discover the secrets of organic pest control for flowers.
Attract Beneficial Insects
Understanding the Role of Beneficial Insects
Beneficial insects play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy garden ecosystem, as they help control pest populations naturally. These insects, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and hoverflies, prey on common garden pests like aphids, mites, and caterpillars, keeping their populations in check. By attracting and supporting beneficial insects, you can reduce the need for harmful pesticides and promote a more balanced and sustainable garden environment.
Creating a Habitat for Beneficial Insects
To attract beneficial insects to your garden, it is important to create a suitable habitat for them. Provide a diverse range of flowering plants that produce nectar and pollen, as this will attract and sustain these helpful insects. Incorporating native plants into your garden is particularly beneficial, as they are well-adapted to attracting local beneficial insects. Additionally, consider adding water sources like birdbaths or shallow dishes of water, which can provide drinking spots for beneficial insects.
Selecting Plants that Attract Beneficial Insects
When choosing plants for your garden, focus on those that are known to attract beneficial insects. Some popular choices include dill, fennel, yarrow, and clover. These plants, with their attractive flowers and aromatic foliage, serve as beacons for beneficial insects. By strategically planting them throughout your garden, you can encourage these helpful insects to take up residence and contribute to pest control efforts.
Avoiding Pesticides that Harm Beneficial Insects
While it may be tempting to reach for commercially available pesticides when faced with garden pests, it is important to remember that these products can harm beneficial insects. Chemical pesticides are indiscriminate in their effects and can kill not only the pests but also the beneficial insects in your garden. Instead, opt for organic and natural pest control methods that specifically target the pests while sparing the beneficial insects. By avoiding harmful pesticides, you can preserve a thriving population of beneficial insects in your garden.
Companion Planting
Complementary Plant Combinations
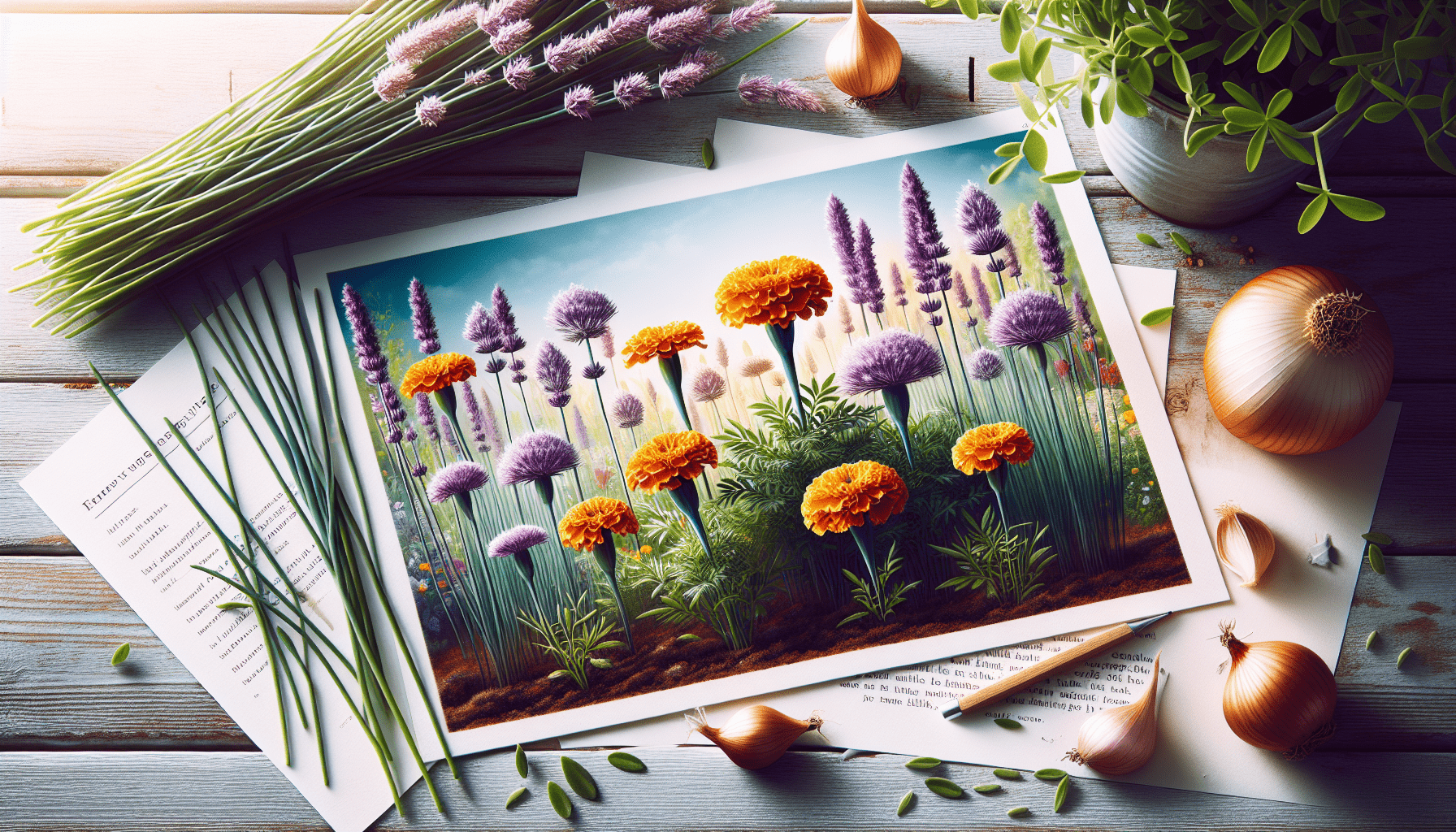
Companion planting involves strategically placing plants that complement and benefit each other when grown together. For pest control, certain plant combinations can deter pests or attract natural predators that feed on them. For example, planting marigolds alongside tomatoes can deter nematodes, while growing basil near beans can repel aphids. Understanding which plants work well together and the specific benefits they provide can help you create a more pest-resistant garden.
Deterrent Plant Combinations
In addition to complementary plant combinations, there are specific plant combinations known to repel pests due to their natural properties or scents. For instance, planting garlic or onions near roses can deter aphids, while planting mint around cabbage can repel cabbage moths. By incorporating these deterrent plant combinations into your garden, you can reduce pest infestations and minimize the need for chemical interventions.
Benefits of Companion Planting for Pest Control
Companion planting offers numerous benefits for pest control in your garden. By combining plants that deter pests or attract beneficial insects, you can create a naturally balanced environment that reduces the need for chemical pesticides. Companion planting not only minimizes the risk of pest damage but also promotes biodiversity, improves soil health, and enhances the overall resilience of your garden.
Tips for Effective Companion Planting
To make the most of companion planting for pest control, consider the specific needs and characteristics of the plants you are growing. Research and plan which combinations are most effective for deterring pests or attracting beneficial insects based on your garden’s specific pest challenges. Rotate plantings each season to avoid building up pest populations or depleting the soil’s nutrients. Additionally, pay attention to the spacing and compatibility of companion plants, ensuring they have enough room to grow and thrive together.

Encouraging Natural Predators
Identifying and Encouraging Natural Predators
Natural predators such as birds, bats, frogs, and beneficial insects can be incredibly effective in controlling garden pests. To encourage these predators, create a garden environment that provides suitable shelter, nesting sites, and food sources. Install birdhouses, bat boxes, and frog ponds to attract these natural predators. Additionally, avoid using chemical pesticides that may harm or deter these helpful creatures. By promoting a habitat that attracts natural predators, you can significantly reduce pest populations and achieve a more balanced ecosystem in your garden.
Providing Shelter and Food Sources
To attract natural predators, it is crucial to provide them with a habitat that meets their needs. Creating diverse microhabitats, such as rock piles, log piles, and dense shrubbery, can offer shelter and nesting sites for predatory animals and insects. Additionally, incorporate plants that produce seeds or berries as a food source for birds. By providing the necessary shelter and food, you can entice natural predators to take up residence in your garden and help control pest populations.
Introducing Beneficial Organisms
In addition to natural predators, introducing beneficial organisms can provide effective pest control in your garden. For example, releasing nematodes can help control soil-dwelling pests like grubs and caterpillars. Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites are also commercially available beneficial insects that can be introduced to combat aphids, mites, and thrips. Before introducing these organisms, ensure that the conditions in your garden are suitable for their survival and reproduction.
Creating Pest-Free Zones
To ensure the effectiveness of natural predators, create pest-free zones or designated areas where these predators can thrive without significant competition from pests. These areas can be created using physical barriers such as netting or screens, or by selectively planting pest-resistant varieties. By providing safe havens for natural predators to flourish, you can maximize their impact on pest control and reduce the need for additional interventions.
Crop Rotation
Understanding the Importance of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an essential practice for maintaining soil health and managing pest populations in your garden. By rotating the crops you grow in different areas each year, you can disrupt the life cycles of pests that rely on specific plant species. This helps to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil, reducing the need for chemical pesticide use and promoting a healthier garden ecosystem.
Managing Pest Build-Up through Rotation
Crop rotation involves dividing your garden into different sections and rotating crops based on their families or characteristics. This disrupts the continuous presence of host plants for specific pests, preventing them from establishing and multiplying. For example, if you planted tomatoes in one area last year and pests like tomato hornworms were a problem, you can move tomatoes to a different section the following year to prevent the pests from finding their favorite food again.
Planning and Implementing a Crop Rotation Schedule
To effectively implement crop rotation, it is important to plan and follow a rotation schedule. Consider the pest pressure in your garden, the life cycles of pests, and the specific needs of different crops when designing your rotation plan. Keep in mind that some plants, such as legumes, can improve soil fertility by fixing nitrogen, while others may be more susceptible to particular pests or diseases. By carefully planning and implementing a crop rotation schedule, you can minimize the risk of pest buildup and maintain a healthy garden.
Benefits of Crop Rotation for Pest Control
Crop rotation offers a range of benefits for pest control in your garden. By disrupting the life cycles of pests and diseases, you can reduce their populations naturally without relying on chemical interventions. Additionally, crop rotation promotes better soil fertility and structure, leading to healthier plants that are more resilient against pests. By adopting crop rotation as part of your gardening practices, you can achieve long-term pest control and maintain a thriving garden ecosystem.

Mulching and Weed Control
Benefits of Mulching
Mulching offers numerous benefits for pest control and garden health. By covering the soil surface with a layer of organic mulch, you can suppress weed growth, retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and improve overall soil health. Mulch acts as a physical barrier, preventing pests from reaching the soil and laying eggs, while also reducing the need for herbicides. Additionally, organic mulch breaks down over time, adding nutrients to the soil and promoting beneficial microbial activity.
Using Organic Mulch for Pest Control
When choosing mulch for pest control, opt for organic materials like straw, wood chips, or leaf litter. These materials not only provide the necessary physical barrier but also support beneficial soil organisms that aid in pest control. Avoid using mulch made from diseased plant material or invasive species, as this can introduce pests and diseases into your garden. Apply a thick layer of mulch around plants, leaving a small gap around the stems to prevent moisture retention and stem rot.
Effective Weed Control Strategies
Weeds can harbor pests and compete with your garden plants for nutrients and resources. Effective weed control strategies are essential for maintaining a healthy and pest-resistant garden. Manual weed pulling or hoeing can be effective for small gardens or specific areas, but for larger areas, consider using mulch to suppress weed growth. Mulching not only smothers weeds but also prevents their seeds from germinating. Regularly inspect your garden for any emerging weeds and promptly remove them to prevent competition and reduce pest habitats.
Preventing Pest Infestation with Mulching
Mulching not only aids in controlling weeds but can also help prevent pest infestations. By creating a barrier between pests and the soil, mulch reduces the chances of pests accessing their preferred host plants or laying eggs in the soil. Additionally, mulch helps regulate soil moisture, reducing the risk of pests that thrive in overly dry or waterlogged conditions. By incorporating mulching into your pest control strategies, you can create a healthier garden environment that is less susceptible to pest damage.
Natural Homemade Sprays
Essential Oil Sprays for Pest Control
Essential oils can be used to create effective homemade sprays for pest control. Certain essential oils, such as neem oil, peppermint oil, and thyme oil, have insecticidal properties that repel or kill common garden pests. Dilute the essential oil with water or a carrier oil and apply it directly to affected plants, focusing on areas where pests are most prevalent. Essential oil sprays are a natural and safe alternative to chemical pesticides and can be used throughout the growing season as needed.
Garlic and Onion Sprays for Pest Deterrence
Garlic and onion sprays are effective deterrents against many garden pests. To make a garlic or onion spray, blend a few cloves of garlic or onions with water and strain the mixture. Dilute the resulting liquid with water and apply it as a spray on plants. The strong odor of garlic and onions repels pests like aphids, beetles, and caterpillars. Regular applications of garlic or onion sprays can deter pests and help protect your flowers and plants.
Soap and Water Solutions for Pest Management
A simple and effective homemade pesticide can be made using soap and water. Mix a few tablespoons of liquid soap, such as Castile soap, with water and transfer the solution to a spray bottle. Spray the soapy water directly on the pests, including aphids and spider mites, as well as their eggs. The soap disrupts the pests’ outer membrane, causing dehydration and eventual death. Take care to avoid excessive soap concentration, as this can damage delicate plant tissues.
Herbal Sprays to Repel Garden Pests
Certain herbs, such as basil, mint, and rosemary, can be used to make effective homemade sprays to repel garden pests. Steep a handful of fresh herbs in hot water, strain the liquid, and dilute it with water. Transfer the herbal liquid to a spray bottle and apply it to affected plants. The strong scent of these herbs acts as a natural deterrent for pests. Regular and timely applications of herbal sprays can help deter pests and protect your flowers from damage.
Physical Barriers
Installing Fences and Meshes
Installing physical barriers like fences and meshes can be an effective way to prevent larger pests, such as rabbits, deer, and birds, from accessing your garden. Choose materials that are sturdy and durable, ensuring they create a secure boundary around your garden. Additionally, bury the fences or meshes slightly underground to prevent burrowing animals from entering. Regularly inspect and maintain these barriers to ensure they remain intact and effective.
Using Row Covers for Protection
Row covers are lightweight, breathable fabrics that can protect your plants from insect pests while allowing sunlight, water, and air to pass through. These covers act as a physical barrier, preventing pests like aphids, caterpillars, and beetles from reaching your plants. Secure the row covers over your garden beds using stakes or wire hoops. Be sure to remove the covers when necessary for pollination or when plants need access to sunlight. Row covers are a valuable tool for protecting your flowers from pests throughout the growing season.
Netting and Other Barrier Techniques
Netting can be used to protect individual plants or small areas from bird and insect damage. Choose netting with small mesh sizes to ensure pests cannot penetrate. Drape the netting over the plants, securing it at the base to prevent pests from accessing your flowers. Other barrier techniques, such as using collars around the stems of vulnerable plants or creating physical barriers around pots or containers, can also provide effective protection against pests.
Building Raised Beds for Pest Prevention
Raised beds offer several advantages for pest prevention. By elevating your garden beds, you can reduce the risk of soilborne pests and diseases. The raised height also makes it more challenging for certain pests, such as slugs or snails, to access your plants. Additionally, you can install physical barriers, such as mesh or liners, at the bottom of the raised beds to prevent burrowing pests from entering. Raised beds provide an opportunity to create a controlled environment that minimizes pest damage and enhances the overall health of your flowers.
Handpicking and Manual Removal
Identifying Common Garden Pests
To effectively handpick and manually remove garden pests, it is crucial to be able to identify common pests that may be present in your garden. Some examples of common garden pests include aphids, caterpillars, slugs, snails, and beetles. By learning to identify these pests and their feeding patterns, you can take appropriate action to remove them from your plants without causing harm to the surrounding flowers.
Safe Techniques for Handpicking
Handpicking is a simple and effective method for managing pest populations in your garden. Inspect your plants regularly, paying attention to the undersides of leaves and the stems where pests often hide. Use gloves or tweezers to carefully remove pests, dropping them into a bucket of soapy water or disposing of them far away from your garden. Handpicking can be particularly useful for larger pests like caterpillars or beetles that are easily spotted and removed.
Removing Pests without Harming Flowers
When manually removing pests, take care not to harm the surrounding flowers or beneficial insects. Gentle handling and precise removal techniques are essential to minimize any potential damage. If necessary, use a soft brush or toothbrush to dislodge pests from delicate flowers, taking care to catch them without damaging the plant. By being mindful of your actions and taking precautions, you can effectively remove pests while preserving the health and beauty of your flowers.
Utilizing Water Sprays for Pest Control
Water sprays can be an effective method for dislodging and removing pests from your plants. Use a strong stream of water from a garden hose to spray infested plants, focusing on areas where pests are concentrated. This method works particularly well for soft-bodied pests like aphids or spider mites. The force of the water will knock pests off the plants, preventing them from causing further damage. Regularly repeat this method as needed to keep pest populations under control.
Soil Amendment and Organic Fertilizers
Improving Soil Health for Pest Resistance
Healthy soil is the foundation of a thriving garden and can help plants resist pest attacks. By improving soil health through proper amendment and maintenance, you can create an environment that is less conducive to pests. Regularly test your soil to determine its nutrient levels and make any necessary amendments to optimize its fertility. Incorporating organic matter, such as compost, into your soil can improve its structure, drainage, and nutrient-holding capacity, promoting strong plant growth and resilience against pests.
Using Compost and Organic Fertilizers
Compost and organic fertilizers provide plants with slow-release nutrients that promote healthy growth and pest resistance. Apply compost to the soil surface or incorporate it into planting holes to provide a steady supply of organic matter. Organic fertilizers, such as bone meal or fish emulsion, can be applied according to package instructions to supplement nutrient levels. These natural amendments improve soil fertility, supporting plants in their defense against pests and diseases.
Applying Beneficial Soil Amendments
In addition to compost and organic fertilizers, there are various beneficial soil amendments that can strengthen your plants’ ability to resist pests. For example, adding beneficial nematodes to your soil can help control pests like grubs and caterpillars. Diatomaceous earth, a natural sedimentary rock, can be sprinkled around plants to deter crawling pests like slugs and snails. Applying these beneficial amendments according to package instructions can provide long-lasting pest control benefits.
Promoting Strong Plant Growth to Resist Pests
Plants that are healthy and robust are better equipped to resist and recover from pest damage. To promote strong plant growth, ensure your flowers receive adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients. Regularly monitor for signs of nutrient deficiencies, disease, or stress, and take appropriate action to address these issues promptly. By maintaining optimal growing conditions and supporting strong plant growth, you can boost their natural defenses against pests and minimize the risk of infestations.
Traps and Lures
Different Types of Insect Traps
Insect traps are useful tools for monitoring and managing garden pest populations. There are various types of traps available, including sticky traps, pheromone traps, and light traps. Sticky traps capture flying insects like aphids, whiteflies, or fruit flies, while pheromone traps attract and trap specific pests using sex pheromones. Light traps are effective for attracting and trapping nocturnal pests like moths. Using a combination of these traps can help you identify pest populations and monitor their activity in your garden.
Effective Baits and Lures
Baits and lures can be used in traps to attract and trap specific garden pests. For example, fruit fly traps can be baited with a mixture of apple cider vinegar and dish soap to attract and drown these pests. Slugs and snails can be lured into traps using beer or a mixture of yeast, sugar, and water. By strategically placing these baits and lures in your garden, you can actively control pest populations and prevent further damage to your flowers.
DIY Traps for Homemade Pest Control
If you prefer to make your own insect traps, there are various simple and effective DIY options available. For example, a shallow dish filled with soapy water can be used to trap and drown pests like aphids or whiteflies. Tuna cans or yogurt containers filled with beer can act as traps for slugs and snails. Creating these homemade traps allows you to customize them according to your garden’s specific pest challenges and effectively manage pest populations.
Monitoring and Managing Traps for Best Results
Regular monitoring and management of traps are crucial for achieving the best results in pest control. Check traps regularly to assess the level of pest activity and determine if any adjustments are needed. If traps become too full, empty and clean them to maintain their effectiveness. Monitor the effectiveness of baits, lures, and pheromones, and replace them as needed. By staying proactive in trap management, you can effectively control pest populations and prevent further damage to your flowers.
In conclusion, organic pest control methods offer a natural and sustainable approach to protecting your garden and flowers from pests. By understanding the role of beneficial insects, utilizing companion planting, encouraging natural predators, practicing crop rotation, mulching, using natural homemade sprays, employing physical barriers, handpicking and manual removal, amending the soil, and utilizing traps and lures, you can effectively manage pests while promoting a healthy and thriving garden ecosystem. With these techniques, you can enjoy beautiful and pest-free flowers while minimizing the need for harmful chemical pesticides.